
Laser metal cutting – Key advantages and characteristics
Today’s technology enables sophisticated metalworking processes, whether cutting, welding or other operations. One of the most modern processing methods, in other words, metal cutting methods, is laser metal cutting.
The term laser is an acronym that comes from the English-speaking area, meaning “Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation”. The laser is nothing but a light oscillator that allows focusing on a point of a very small diameter, smaller than 1 mm.
The laser cutting alone is the thermal material cutting process, in which the laser source, i.e., the resonator creates a laser beam that is, by means of a mirror, carried out in the cutter head of the machine, focusing on a point of very small diameter.
Laser metal cutting– application and benefits
Due to its high precision, laser cutting has been used in many branches of the industry, some of which are metallurgy, electronics, shipbuilding etc.
Laser metal cutting offers many benefits, and some of them are the following:
- low heat input on metal
- small deformation of the metal
- high speed
- high quality cut
- flexibility
- cost-effectiveness
- precision
The principles of laser metal cutting
Laser metal cutting can be done by:
- CO2 lasers: used when drilling, cutting, marking, engraving
- Nd lasers: most commonly used for drilling. They are characterized by high energy impulses and low speed repetitions
- Nd – YAG lasers: used for drilling, engraving and adjustment. They use very high energy impuls
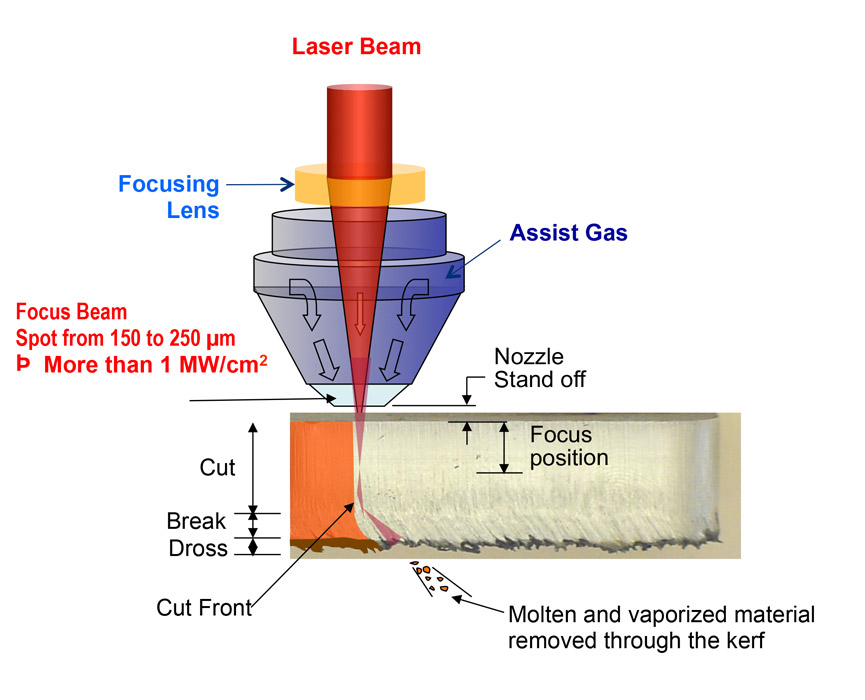
The illustration of the work of a laser cutting machine
Laser cutting is a thermal process that starts by heating and focusing laser beam (density ranges around 104 Wmm-2) in combination with gas (active or inert). The laser beam melts metal that is being sliced, and gas with its current eliminates the liquefied metal. Laser metal cutting begins by drilling a hole in the metal, and hole drilling can take up to 15 seconds depending on the thickness of the metal. The laser beam applied during the laser cutting process is parallel to a thickness of 1.5 to 12.5 mm.
Laser metal cutting is one of the variations in laser cutting.
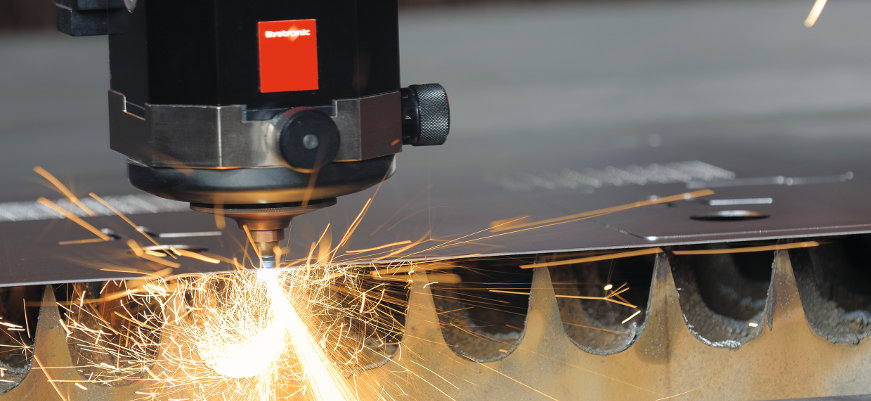
An example of a metal cut by a laser is shown below.
Characteristics of laser metal cutting
The precision that can be achieved by laser metal cutting is up to 0.01. The amount of heat that is being introduced during the cutting process, can be seen in the table. The amounts are given in watts [W].
Speed is one of the benefits of laser cutting.
The table below shows the time in minutes needed to cut an inch of material.
| Material | Material thickness (mm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 1 | 2 | 3.5 | 6 | |
| Stainless steel | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 500 | 250 |
| Aluminum | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 3800 | 10000 |
| Mild steel | - | 400 | - | 500 | - |
| Titanium | 250 | 210 | 210 | - | - |
Laser metal cutting has several parameters that can be changed, and one of the most important is impulse, that is, continuous beam. Peak power at impulse laser cutting or average power at continuous laser cutting determines penetration. Continuous beam is applied to smooth and thicker material, while impulse beam is used for precise cutting. Comparison of the continuous and the impulse beam cuts can be seen in the photo.
Conclusion
One of the most modern methods of machine metal cutting is laser metal cutting.
The price of laser metal cutting depends on the specific requirements, ie, on the type, the quality and the thickness of the material being cut.


